Headache & Migraine
If you notice any of the following symptoms, it may be serious. Consult your doctor.
With these symptoms, CT-scan or MRI-scan is required.
Types of headache:There are two broad types of headache:
1) Primary – where exact reasons are not known. There are many hypotheses, postulations, but the exact cause of these types of headaches is still not understood. The common headaches of these categories are following:- Tension-type headache
- Migraine
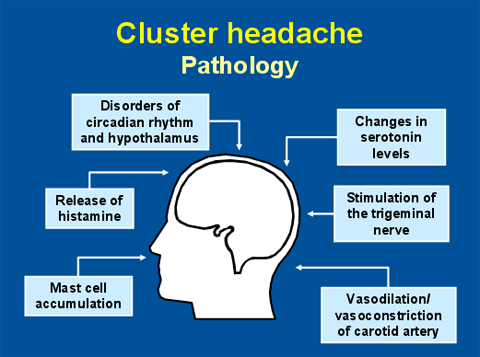
- Cluster headache
- Cervicogenic headaches due to pathologies in the neck
- Occipital Neuralgia (Third occipital neuralgia is one of them)
Tension-type headache is the most common type of primary headache. It is a pain or discomfort in the head, scalp or neck and is often associated with muscle tightness in these areas.
For most of the population, the first onset of TTH is before the second decade of life. The peak prevalence appears to be between 30-39 years of age. The lifetime prevalence ranges between 30%-78%. It is seen in both sexes with female preponderance. The studies show that there is a slight decrease in the occurrence with advancing age.
Classification- Episodic TTH (ETTH):- Infrequent episodic, Frequent episodic
- Chronic TTH (CTTH)
- Associated with peri cranial tenderness
- Not associated with peri cranial tenderness
Interventional
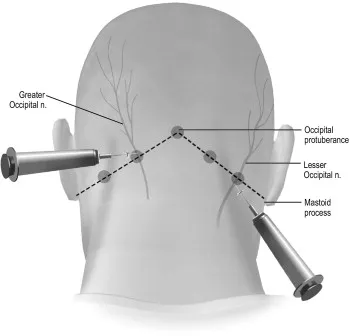
1.Greater and lesser occipital nerve injections using local anesthetic with or without corticosteroids give a positive effect and short-term relief of CEH. Many authors consider entrapment of the greater occipital nerve to be one of the major underlying causes of CEH.
2. Injection into the atlanto-axial joint with a local anesthetic andcorticosteroid, in patients with CEH, can be done ifclinical picture is suggestive of atlantoaxial joint pain. There was nostatistically significant difference after 6 months in this retrospectivestudy.’
3. C2-3 zygapophysial joint, investigators from one study reported that some patients could obtain relief from intra-articular injection of steroids.’ Third occipital nerve block with local anaesthetic and/or steroid can be given for C2-C3 facet joint.
4. Local injection of the ramus medialis of the cervicalramus dorsalis (cervical medial branch block) can also be done for diagnostic purpose
2. In a prospective study in patients with CEH according to the criteria of Sjaastad, receiving RF treatment of the ramus medialis (medial branch) of the cervical ramus dorsalis, the results were outstanding to good in 65%, average in 14%, and no improvement was seen in 21% of the patients, with an average follow-up of 16.8 months.
Microsurgical decompression of the C2 ganglion spinale. During microsurgical decompression of the ganglion spinale (DRG), ligament structures and veins around the ganglion were “removed” by means of electrocoagulation.
Cervicogenic Headache
Types
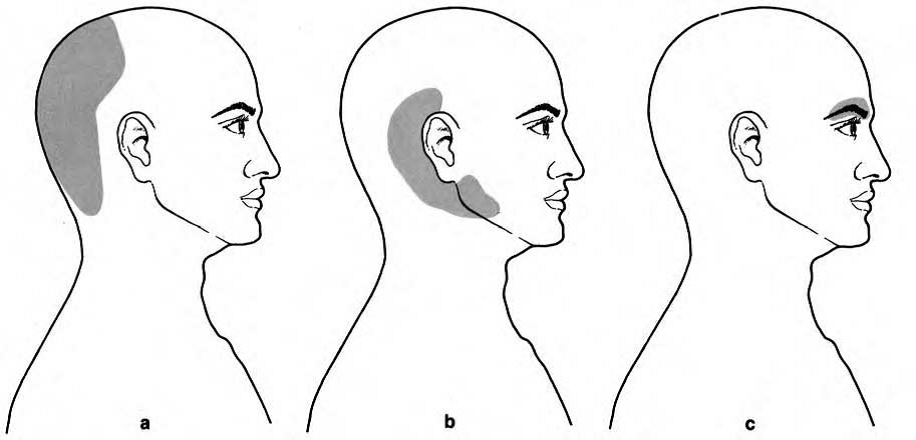
Three different aspects of cervicogenic headaches can be described according to the area of reference of pain
(a) occipital
(b) Occipital temporal maxillary form.
(c) supraorbital form . They overlaps frequently.
Secondary Headaches
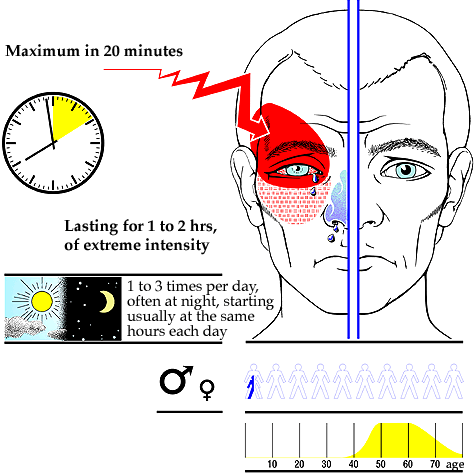
Diagnosis of Cluster Headache
It is a primary headache, so there is no blood test or imaging to diagnose it. Instead, a neurologist or pain specialist only diagnoses it based on clinical features. But the patient might need to do some blood tests and imaging of the head (CT or MRI) to rule out other causes of secondary headache.
Treatment Of Cluster Headache